Thermal spray coating leads to several processes in which a substrate is coated to enhance working performance. Many types of coating materials can be used by thermal spray processes. Coatings can classify in thickness from a thousandth of an inch up to an eighth of an inch. Thermal spray coatings have been utilized to protect parts from damage, abrasion, corrosion, high temperatures, etc. also to create dimensions on undersized parts.
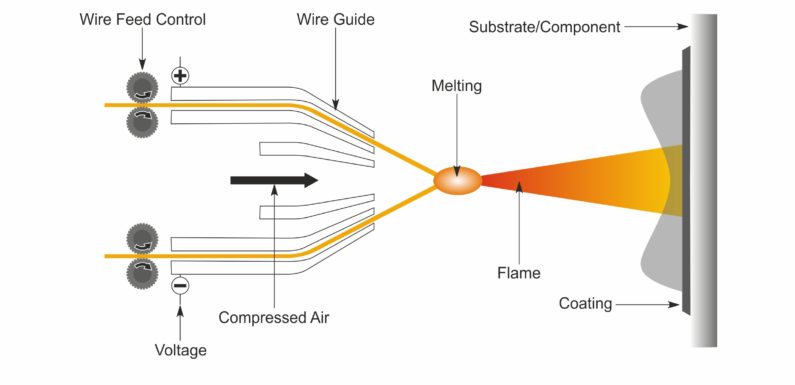
Coating methods involve the removal of coatings from a current of high velocity finely distributed particles in a molten or semi-molten state affecting the substrate. These processes use delicate powdered source material either sometimes metal wire that is molten including broken into fine droplets. The coating gun combines thermal energy to deliver the materials to a plastic or molten condition than accelerates these materials at high velocities toward the substrate.
There are many various types of Thermal Spray Coating processes. They oppose how they apply thermal & kinetic energy to the source material, the structure of the source material (powder or wire) & the relative velocities also temperatures of the flame.
Separately process has advantages including disadvantages, and some are optimized for certain types of coatings. Thermal Spray Coatings are applied for accurate control of coating properties and thickness and process repeatability. We rely on advanced process control systems to ensure that the quality of the coatings is optimized. Thermal spray guns can also be used by hand controlled guns.
Thermal Spray Coating Technology
- Coating material begins as powder or wire form. A wide range of matters are available
- The thermal spray gun produces energy to the coating material particles also transports the coating to the part. Energy can be thermal (heat) either kinetic (velocity). Many different technologies are available:
- HVOF
- Plasma Spray
- Flame Spray
- The thermal spray gun is regulated by an industrial worker for precise control of the coating
- As the particles of molten material hit the substrate, they collapse into smoothed droplets furthermore in lamellar layers forming a cohesive coating structure.
- Cooling of the substrate is applied to control the temperature gain of the substrate.
Identification of Thermal Spray Technologies
This table provides a summary of typical industry values for various thermal spray coating techniques.
| Process | HVOF | PLASMA | FLAME |
| Particle velocity (m/s) | 800 | 300 | 40 |
| Particle/Gas Temp (°C) | 3,000 | 14000< | 3000 |
| Adhesion (psi) | >10,000 | >700 | 1000 |
| Oxides (%) | <2 | <3 | 12 |
| Porosity (%) | <2 | <5 | <15 |
Parameters of Process Control
- powder Material
- Composition
- Geometry
- Controlled feed rate in a carrier gas
- Thermal Spray Gun
- Acceleration
- Thermal Energy to particles
- Particle exit velocity
- Molten and semi-molten particles travel to the part surface
- Gas flow controls
- Standoff distance
- Traverse rate
- Multiple coating passes to build the required thickness
- Coating angle
- Substrate surface preparation
- Cleaning
- Surface roughness
- Masking of areas that must not be coated
- Substrate temperature control
- Cooling systems
- Localized temperature changes
- Coating system controls
- Acoustical booth
- Dust collector and recycling coating materials
Process Steps
- Part Cleaning/Degreasing
- Masking
- Surface Preparation of surfaces to be coated
- Blasting
- Demasking/Cleaning
- Masking/Preparation for Coating
- Coating
- Demasking
- Secondary operations such as deburring or finishing
- Inspection & Testing